Call Gosu code from Java
Why
Java is trivial to call from Gosu. Just put Java JARs on the Gosu classpath, add Java class usage declaration and you are ready to go.
It is not so straightforward to do opposite, as Gosu relies on its own classloader which makes its magical tricks like Open Type System possible.
As Gosu's syntax is more powerful and less explicit than Java, wouldn't it be nice to be able to write at least parts of your application in it? Here is how you can do it.
Solution overview
General idea is to:
- define Gosu class(es) API(s) as Java interface(s),
- implement this interface in Gosu,
- use Gosu Reflection API to create an instance of Gosu class.
Both Gosu provider and Java consumer will share dependency on the interface defined in Java, which may be distributed as a separate JAR file.
How to set up IntelliJ Idea
- Create new project - choose "Empty".
- Project structure dialog will be displayed.
- Add new Java module "java-api". It will contain Java code defining interface implemented by Gosu service provider.
- Add new Gosu module "gosu-provider".
- It will contain Gosu code implementing interface defined in "java-api" module.
- Select "Dependencies" tab and use green "+" icon on the right size of dependencies list.
- Select "Module dependency" and choose "java-api" from the list.
- Add new Java module "java-consumer".
- It will contain Java code consuming services implemented in Gosu, defined in "gosu-provider" module.
- Select "Dependencies" tab and use green "+" icon on the right size of dependencies list.
- Select "Module dependency" and choose "java-api" and "gosu-provider" from the list.
Make sure your module SDKs are pointing to:
- java-api - Java SDK (1.7 in my case)
- java-consumer, gosu-provider - Gosu SDK
WARNING: I've been experiencing problems with IntelliJ Idea 12.1.6 while trying to make it run. Try your luck with IJ 12.1.4. This is what I used for this example.
Code
ServiceApi.java
This will contain definition of interface offered by our Gosu class. This will be shared between our Gosu provider and Java consumer code.
package sample.api;
public interface ServiceApi {
String execute();
}
ServiceProvider.gs
Here we implement our logic in Gosu.
package sample.provider
uses sample.api.ServiceApi
class ServiceProvider implements ServiceApi {
construct() {
}
override function execute() : String {
return "Hello from Gosu service"
}
}
ServiceConsumer.java
And this how we will initialize Gosu and then instantiate and call Gosu class providing implementation of known interface.
package sample.consumer;
import sample.api.ServiceApi;
import gw.lang.reflect.ReflectUtil;
import gw.lang.Gosu;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ServiceConsumer {
public ServiceConsumer() {
}
public String consume() {
List gosuPath = new ArrayList();
// path to libraries
gosuPath.add(new File("c:/work/projects/sandbox/java-gosu-interop/lib/"));
// path to gosu sources
gosuPath.add(new File("c:/work/projects/sandbox/java-gosu-interop/gosu-provider/src/"));
Gosu.init(gosuPath);
ServiceApi service = (ServiceApi) ReflectUtil.construct("sample.provider.ServiceProvider");
return service.execute();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws URISyntaxException {
ServiceConsumer consumer = new ServiceConsumer();
System.out.println(consumer.consume());
}
}
You should end up with something like this:
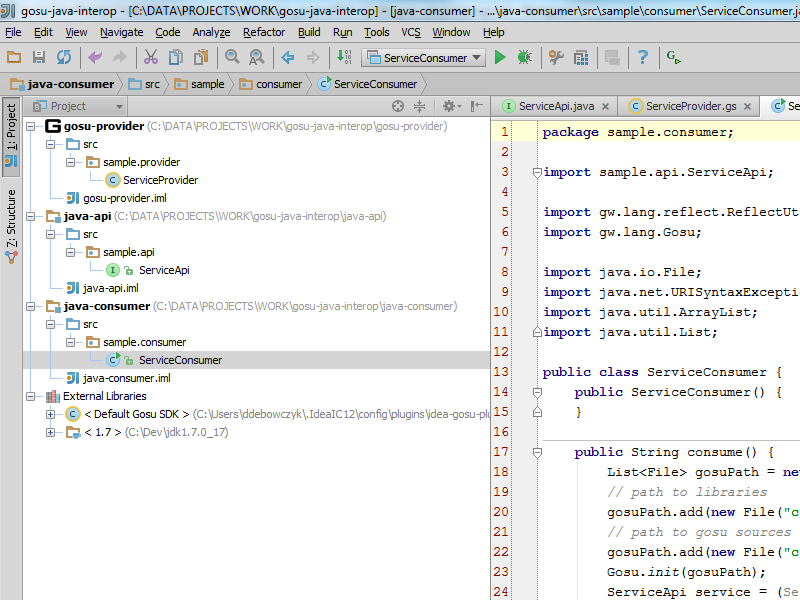
To run your Java ServiceConsumer which executes Gosu code:
- open configurations (Run > Edit configurations),
- add new Application,
- select ServiceConsumer as main class,
- set "Use classpath of module" to "java-consumer" module,
- hit "Run".
You will find source code for this at GitHub.
Have fun.
CREDITS:
- Idea of the solution comes from: (https://gist.github.com/am2605/1577272)